 Ongoing
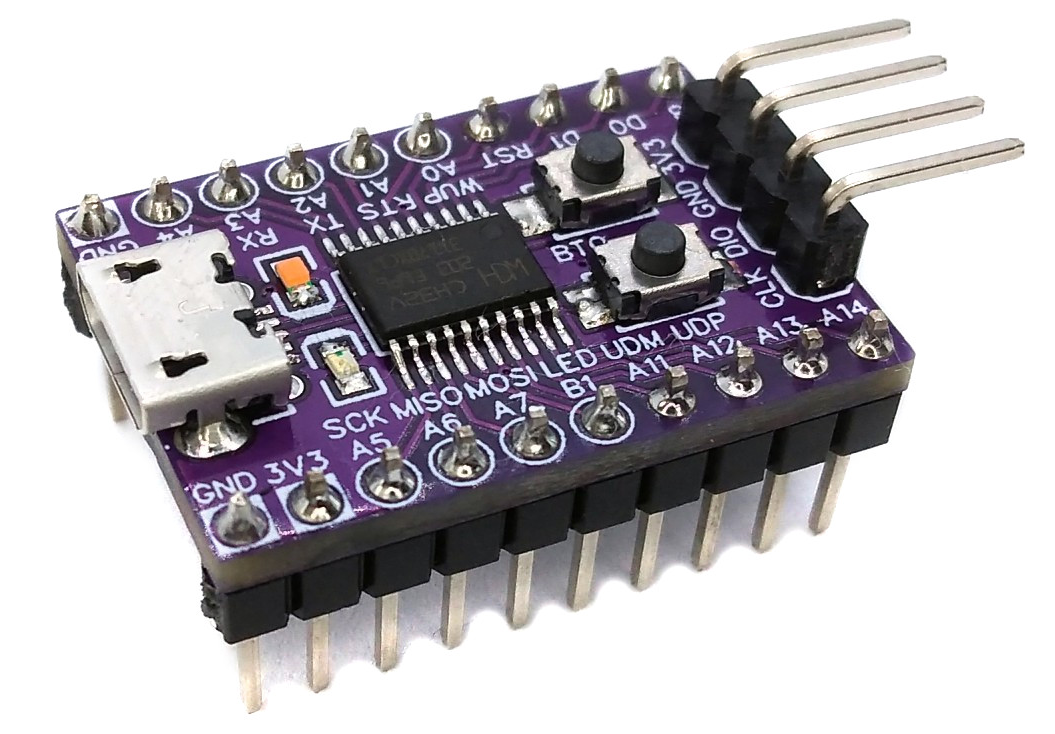
OngoingCH32V203 F6P6 Development Board
STDCH32V203 F6P6 Development Board
2.8k
0
0
0
Mode:Full
License
:CC-BY-SA 3.0
Creation time:2023-06-22 17:29:25Update time:2023-09-24 07:58:09
Description
Design Drawing
 The preview image was not generated, please save it again in the editor.
The preview image was not generated, please save it again in the editor.BOM
 Bom empty
Bom empty Clone
CloneAdd to Album
0
0
Share
Report
Project Members
Followers0|Likes0
Related projects
 Empty
Empty


Comment