 Ongoing
OngoingNext-Generation Open-Source Robotics Kicker Circuit 2026
PRONext-Generation Open-Source Robotics Kicker Circuit 2026
License
:MIT License
Description
Next-Generation Open-Source Robotics Kicker Circuit
High-Speed Constant Current Charging Edition
Overview
Building upon the success of our original open-source kicker circuit, this new iteration represents a massive leap in performance and responsiveness. While the previous design revolutionised accessibility for hobbyist teams, its 2–3 second charge time presented a bottleneck in fast-paced competitive environments.
This upgraded design introduces a sophisticated constant current charging architecture, reducing cycle times to under 100ms. By slashing the recharge time by over 95%, this circuit allows robots to perform rapid-fire sequences and maintain offensive pressure that was previously impossible.
Features and Key Design Elements
-
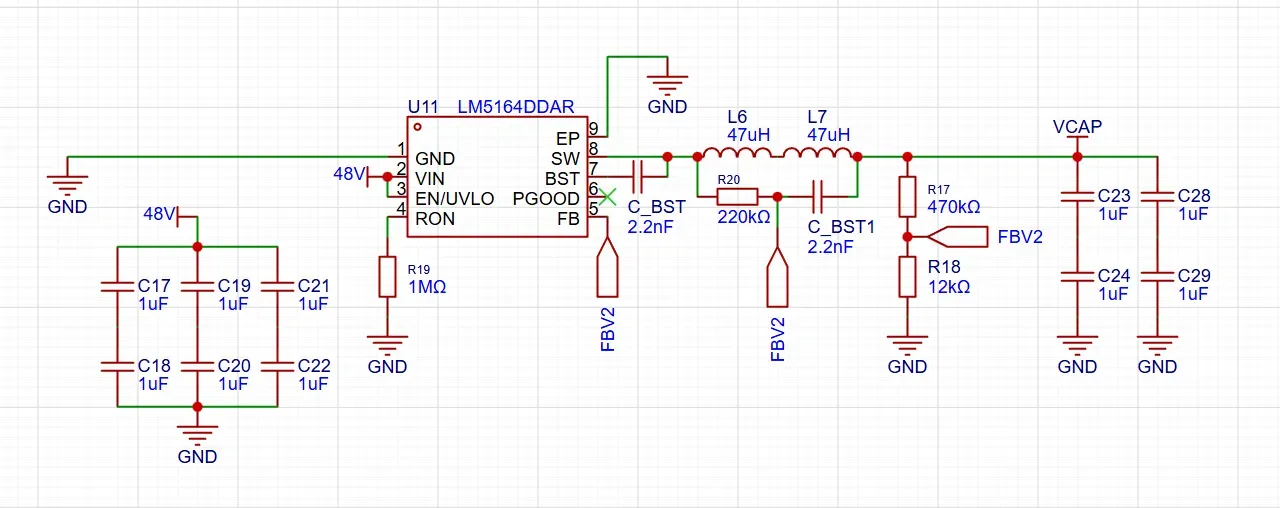
Ultra-Fast Cycle Times Utilizes the LM5164DDAR synchronous buck/boost controller to implement a constant current charging profile. This ensures the capacitor bank is replenished in <100ms, compared to the multi-second delay of the previous purely XL6019E1-based design.
-
Constant Current Regulation Unlike the voltage-limited approach of the original project, the new design maintains a steady current flow throughout the entire charging cycle. This prevents input voltage sag and protects the robot’s main battery from high-current spikes.
-
Enhanced Energy Density Retains the high-performance, low-ESR capacitor bank (~40J–46J capacity) but optimizes the charging curve to reach target voltage with surgical precision, maintaining the same ±0.5V shot consistency.
-
Backwards Compatibility The modular interface remains 3.3V/5V logic tolerant, ensuring that teams currently using the v1.0 design can upgrade to the high-speed version with minimal firmware or wiring changes.
Detailed System Design
The architecture has been redesigned to prioritize thermal efficiency and charging speed while maintaining the tripartite modularity (Storage, Logic, and Safety) of the original.
Advanced Charging & Conversion
-
The LM5164DDAR Engine: The heart of the new design is the LM5164DDAR high-voltage synchronous converter. By utilizing its advanced current-sensing capabilities, the circuit operates in a constant-current mode. This allows the capacitors to soak up energy at the maximum safe rate allowed by the components, bypassing the "diminishing returns" curve of traditional boost converters.
-
Rapid Replenishment: By delivering a consistent amperage, the system avoids the slow "trickle" phase at the end of a charge cycle. This results in the move from a 3-second "ready" light to a virtually instantaneous 0.1-second refresh.
-
Input Stability: The synchronous rectification improves efficiency, reducing the heat generated during the high-speed charging bursts.
Switching & Control Logic
-
High-Speed Gate Drive: We have retained the TC4427A gate driver and IRFP260N MOSFET pairing. This combination has proven exceptionally reliable in the v1.0 design for handling sub-50ns switching, ensuring the energy release into the solenoid is as crisp and powerful as ever.
-
Precision Timing: The discharge pulse duration is still controlled via hardware timers, but the faster recharge allows for complex "dribbling" or multi-stage kick profiles that were previously bottlenecked by charging hardware.
Safety & Monitoring
Safety remains our top priority, especially given the increased power throughput of the new design:
-
Active Thermal Monitoring: Given the high-speed charging cycles, the PCB includes optimized copper pours for heat dissipation and dedicated points for NTC thermistor integration.
-
Legacy Safety Features: The 10kΩ bleeder network remains standard, ensuring the bank discharges safely within 60 seconds when powered down.
-
Fault Detection: The LM5164’s built-in protections provide an extra layer of defense against short circuits and undervoltage conditions.
Applications and Use Cases
-
Dynamic Research: Ideal for testing high-frequency mechanical actuators where the power source must keep pace with rapid-fire control algorithms.
-
Advanced Education: A perfect case study for students to compare Constant Voltage vs. Constant Current charging methodologies in real-world power electronics.
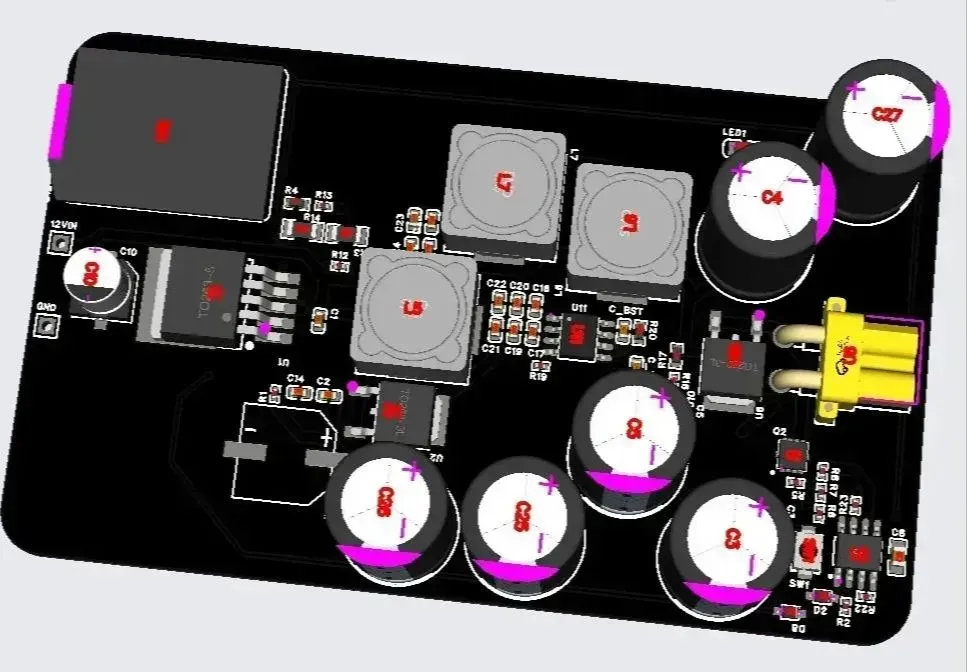
PCB Shell
We have also designed a simple PCB shell to prevent accidental shorting of the high voltage capacitors. The file is available under project attachments.
Conclusion
The new Open-Source Robotics Kicker Circuit isn't just an incremental update; it's a performance overhaul. By moving from a 2–3s charge time to under 100ms, we have removed the primary limitation of open-source kicker systems. Whether you are building your first soccer robot or competing at an international level, this circuit provides the speed, reliability, and power needed to dominate the field.
Design Drawing
 The preview image was not generated, please save it again in the editor.
The preview image was not generated, please save it again in the editor.BOM
 Bom empty
Bom empty Clone
CloneProject Members
 Empty
Empty


Comment